Previously, backup events had to be set up for databases running under Windows. These could be either static events via a web interface or dynamic events using a script utility or procedure command. Although this does not require much effort, an incorrect or missing configuration can prevent a usable backup from being created.
Starting with the upcoming server version 5.7.08, backup events can also take place automatically when a shadow copy is created.
A shadow copy, also known as a “shadow copy” or “volume snapshot,” is a snapshot of one or more mass storage volumes (C:, D:, etc.). These snapshots allow, for example, data backup during operation or the restoration of older versions of the volume.
Backing up a snapshot offers three key advantages over a file-based backup of the original volume:
- block-level backup of a volume is significantly faster
- locked files do not prevent backup
- work can continue without restrictions during the backup
Snapshots are created during operation by either writing all write operations on the volume to an alternative storage area (redirect-on-write) or saving the original content of the respective storage block to the snapshot storage area (copy-on-write) from the time of creation. In order for the snapshot to contain usable data, the volume must be in a consistent state at the time of creation. The file system, metadata, system, and application databases must therefore be prepared accordingly before the snapshot is created.
Windows Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS)
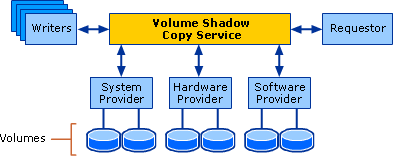
This term refers to a Windows system service that enables the creation and management of snapshots. Many data backup programs now use this service to achieve the above-mentioned advantages. Numerous software components are involved in the creation and use of snapshots using VSS, which can be divided into three categories:
VSS Provider
A “provider” provides the functions for generating, managing, and using snapshots. By default, a “system provider” is available in the Windows operating system that implements shadow copies at the file system level (NTFS or ReFS). Additional providers can also be installed that map the snapshot functionality either in the storage driver layer (“software provider”) or in the storage hardware (“hardware provider”), for example in the controller or in a SAN system.
VSS Requestor
A “requestor” is usually a backup client or agent that communicates with the provider, requests the snapshot, backs up the data, and then removes the snapshot again. In VMware, for example, the installed VMware tools act as requestors to ensure the consistency of VMware’s own snapshots.
VSS Writer
Writers are required to create a consistent state. A VSS writer is responsible for “freezing” the files of its application and returning them to their normal state after the snapshot has been created. A special VSS writer is therefore required for conzept 16 databases.
 (c) by Microsoft Inc.
(c) by Microsoft Inc.VSS with concept 16
Support for shadow copies is fully automatic; the administrator does not need to take anything into account when installing or updating the conzept 16 server. After the database server is started, it registers the VSS writer, which enables the VSS service to put the registered databases into backup mode. For this purpose, there are two program files, c16_serv_vss_w32.dll and c16_serv_vss_w64.dll, which provide the functions of a VSS writer.
VSS support is enabled by default for every registered database. However, it can be disabled for individual databases via the server’s web interface.
VSS Events
The writer receives events from the VSS service that are triggered by operations of a VSS requestor (backup software) and forwarded to the database manager process. Based on these events, the manager then starts and ends backup mode for the affected databases.
Advantages of VSS
- short backup events
A database only needs to be in backup mode at the time the snapshot is created. During the actual backup, the database is in its normal state. The backup event usually takes only a few seconds. - less administrative effort and lower susceptibility to errors
There is no longer any need to enter backup times or integrate the script utility; the backup software automatically controls the backup events. This eliminates the risk of missing backup events or events that do not match the backups. - support for complex solutions
In addition to traditional backup software, VSS is also supported by special data protection products. These include, for example, snapshot and replication applications that run directly on storage systems, backup applications at the virtualization level, and applications such as System Center Data Protection Manager. - backup of standby database possible
In hot standby mode, VSS can also be used to back up the standby database in a consistent state.
Operating systems with VSS
Due to limitations in older Windows versions, conzept 16 supports the Volume Shadow Copy Service from Windows Vista or Windows Server 2008 in 32-bit and 64-bit versions. Of course, this also works with newer versions such as Windows 7, 8, 8.1, and Windows Server 2008 R2, 2012, and 2012 R2.
There is no VSS service under Linux, but snapshots can be created using LVM (Logical Volume Manager). However, the script utility must still be used to switch the database to backup mode before creation (“lvcreate -s …”) and then to cancel this mode again afterwards.
Update: The Windows Server 2003 and 2003 R2 operating systems are also expected to be supported in 32-bit and 64-bit versions.