With CtxDocEdit, conzept 16 provides developers with an object that can be used to implement professional word processing. In addition to functions such as processing different file and image formats or header and footer management, a spell checker is also part of a convenient word processing package.
In the current version of conzept 16, users have the option of activating a spell checker for German and English.
Starting with the upcoming version 5.7.08, conzept 16 will offer the option of expanding the dictionaries with user-defined dictionaries. In this article, I would like to show you how this will work in practice.
Creating a custom dictionary
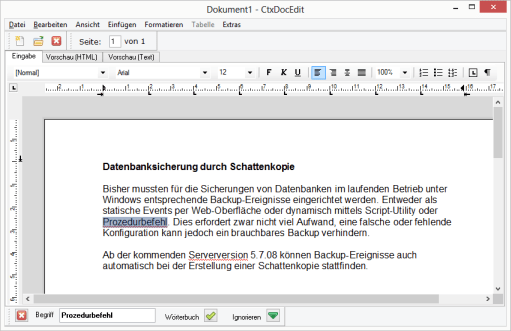
The dictionary forms the basis for the spell checker. When spell checking is active, the words in the text document are compared with the dictionary and incorrect or unknown terms are underlined with a red zigzag line.
In order for the DocEdit object or the underlying spell checker to process the self-created dictionary, it must be in the so-called Tlx format (Text Lexicon). This is a line-based text file. Each term is on a separate line, followed by a tab and a key. The key indicates how the term is to be interpreted.
Adding a custom dictionary
In order for the text to be checked against the custom dictionary, it must be added to the DocEdit object. The addition is done using the new function WinDocUserDictAddName(). It should be noted that this function can also be used to load several dictionaries at the same time. The Spell Checker always takes into account all dictionaries added to the DocEdit object. The function WinDocUserDictRemoveName() is available for unloading individual dictionaries.
Adding words during text entry
Custom dictionaries are also suitable for expanding German or English dictionaries. Since these dictionaries contain the most frequently used words, proper names, abbreviations, or technical terms are usually not recognized and are marked as errors.
We need two functions to implement this. One function identifies the incorrect term, and the other function writes this term to the user-defined dictionary.
Identifying an incorrect word
sub GetMisspelledWord() : alpha
{
// Use the position of the word as the starting point for selection
gCtxDocEdit->cpiSelStart # gCtxDocEdit->cpiMisspelledWordStart(gIdx)
// Set the length of the selection to the length of the word
gCtxDocEdit->cpiSelLength # gCtxDocEdit->cpiMisspelledWordLength(gIdx)
// Determine selected word
return (gCtxDocEdit->CpaSelText);
}The cpiMisspelledWords property can be used to determine whether there are any terms in a text document that need to be corrected. The property returns the number of incorrect terms. Incorrectly spelled or unknown terms are numbered consecutively by the DocEdit object from the beginning to the end of the text.
The above function identifies an incorrect term and highlights it in the text.
The property cpaSeltext returns the selected term as a string. The number of the word is passed to properties cpiMisspelledWordStart and cpiMisspelledWordLength as an argument.
If the user decides to add this word to the user-defined dictionary, the following function is applied.
Adding a word to the dictionary
Sub WriteDictionary(aWord : alpha(84))
{
// Set pointer to the beginning of the file
gFile->FsiSeek(0);
// Import dictionary into memory object
gFile->FsiReadMem(gMem,1,gFile->FsiSize());
// If term does not exist
if (gMem->MemFindStr(1,gMem->SpLen,aWord,_StrFindToken) = 0)
{
// Extend term to include tab, key, and line break
aWord # aWord + mTab + 'i' + mCRLF;
// Set pointer to end of file
gFile->FsiSeek(gFile->FsiSize());
// Write file
gFile->FsiWrite(aWord);
}
// Remove dictionary
gCtxDocEdit->WinDocUserDictRemoveName(mPath + '\MyDic.tlx');
// Add dictionary
gCtxDocEdit->WinDocUserDictAddName(mPath + '\MyDic.tlx');
}After writing the file, the dictionary must be added again so that the spell checker accepts the word as correct.